Real-World First-Line Use of Pertuzumab With Different Taxanes for Human Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor 2-Positive Metastatic Breast Cancer: A Comparative Effectiveness Study Using US Electronic Health Records
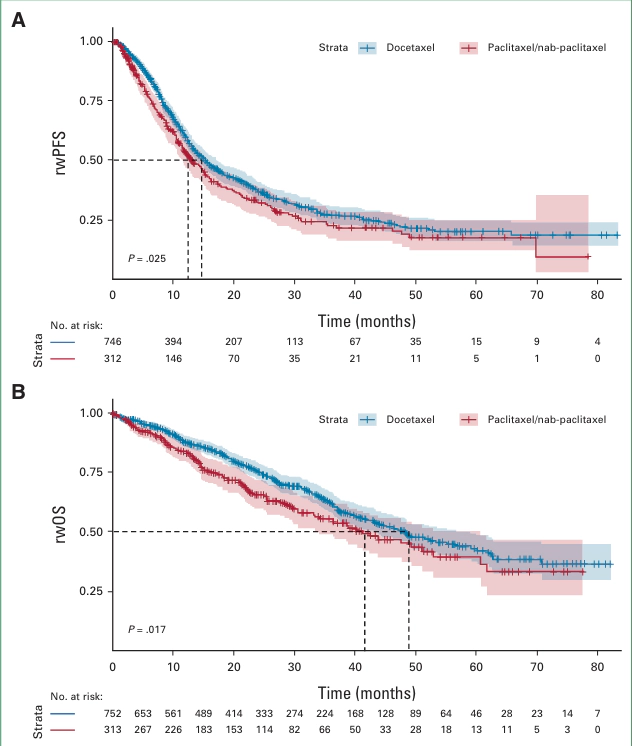 Image credit: Jinjoo Shim
Image credit: Jinjoo ShimAbstract
On the basis of the results from CLEOPATRA, pertuzumab plus trastuzumab and chemotherapy is the first-line standard of care for human epidermal growth factor receptor 2 (HER2)-positive metastatic breast cancer (MBC). However, discrepancies have been reported between clinical trial and real-world outcomes. We report real-world outcomes for patients with HER2-positive MBC treated with first-line pertuzumab plus trastuzumab and a taxane in routine clinical practice in the United States. A retrospective analysis was conducted using electronic health record-derived deidentified data from the Flatiron Health database. Patients were grouped according to the first taxane received (paclitaxel/nab-paclitaxel or docetaxel). Median real-world progression-free survival (rwPFS) and overall survival (rwOS) was estimated using Kaplan-Meier methodology. Subgroup analyses were conducted in patients treated with docetaxel who met CLEOPATRA’s key eligibility criteria. We included 1,065 patients; 313 patients received paclitaxel/nab-paclitaxel and 752 received docetaxel. Patients who received paclitaxel/nab-paclitaxel were older, had a worse Eastern Cooperative Oncology Group Performance Status, and had more recurrent metastatic disease compared with the docetaxel group. After adjustment for potential confounders, similar median rwPFS (inverse probability of treatment weighted average treatment effect for the treated [IPTW-ATT] hazard ratio [HR], 1.09; 95% CI, 0.9 to 1.3; P = .365) and rwOS (IPTW-ATT HR, 1.23; 95% CI, 0.96 to 1.58; P = .101) was observed between treatment groups. In the subgroup of CLEOPATRA-eligible patients, median rwPFS and rwOS were 16.9 months and 57.8 months, respectively. There was no statistically significant difference in real-world outcomes between patients treated with paclitaxel/nab-paclitaxel and those treated with docetaxel. Selecting patients using key CLEOPATRA eligibility criteria resulted in rwPFS and rwOS similar to those observed in CLEOPATRA, highlighting the importance of ensuring similar patient populations when comparing clinical trial and real-world data.