Association of baseline systemic corticosteroid use with overall survival and time to next treatment in patients receiving immune checkpoint inhibitor therapy in real-world US oncology practice for advanced non-small cell lung cancer, melanoma, or urothelial carcinoma
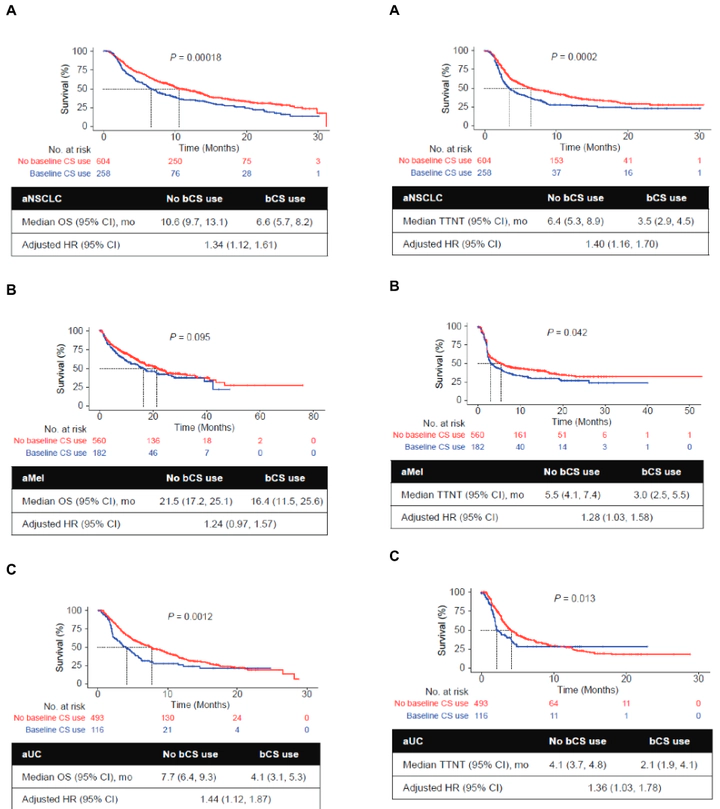 Image credit: Jinjoo Shim
Image credit: Jinjoo ShimAbstract
Immune checkpoint inhibitors (CPIs) have expanded treatment options for patients with solid tumors. Systemic corticosteroids (CSs) have an indispensable role in cancer care, but CS-related immunosuppression may counteract the CPI-driven antitumor immune response. This retrospective study investigated the association between baseline CS use (bCS; ≤14 days before, ≤30 days after CPI initiation) and clinical outcomes in patients with advanced non-small cell lung cancer (aNSCLC), melanoma (aMel), or urothelial carcinoma (aUC). We analyzed data from the Flatiron Health electronic health record-derived de-identified database for adults diagnosed with aNSCLC, aMel, or aUC between January 2011 and June 2017 who received ≥1 CPI monotherapy in any treatment line. Associations of bCS use with overall survival (OS) and time to next treatment (TTNT) were estimated using multivariable Cox proportional hazards models adjusting for demographic and clinical characteristics (i.e., ECOG performance status, site of metastases). In total, 2,213 patients were diagnosed with aNSCLC (n = 862), aMel (n = 742), or aUC (n = 609) and received ≥1 CPI administration. Most patients (67%-95%) received CSs, many during the baseline period (19%-30%). Patients with bCS use had shorter median OS than those with no bCS use for aNSCLC (6.6 vs 10.6 months; P= .00018), aMel (16.4 vs 21.5; P= .095), and aUC (4.1 vs 7.7; P= .0012). bCS use was associated with shorter OS (not significant for aMel) and TTNT in adjusted multivariable analyses, and clinical outcomes were not explained by prior CS use or other measured confounders. These findings suggest a potential association between bCS use and decreased CPI effectiveness, warranting further investigation.